How To Calculate The Ph At Equivalence Point Of Titration
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of 0240 M methylamine CH NH with 0240 M HCI. In the case of titration of weak acid with strong base pH at the equivalence point is determined by the weak acid salt hydrolysis.

Acid Base Titrations Titrations Titration Curve Always Calculate Equivalent Point First Strong Acid Strong Base Regions That Require Different Calculations Ppt Download
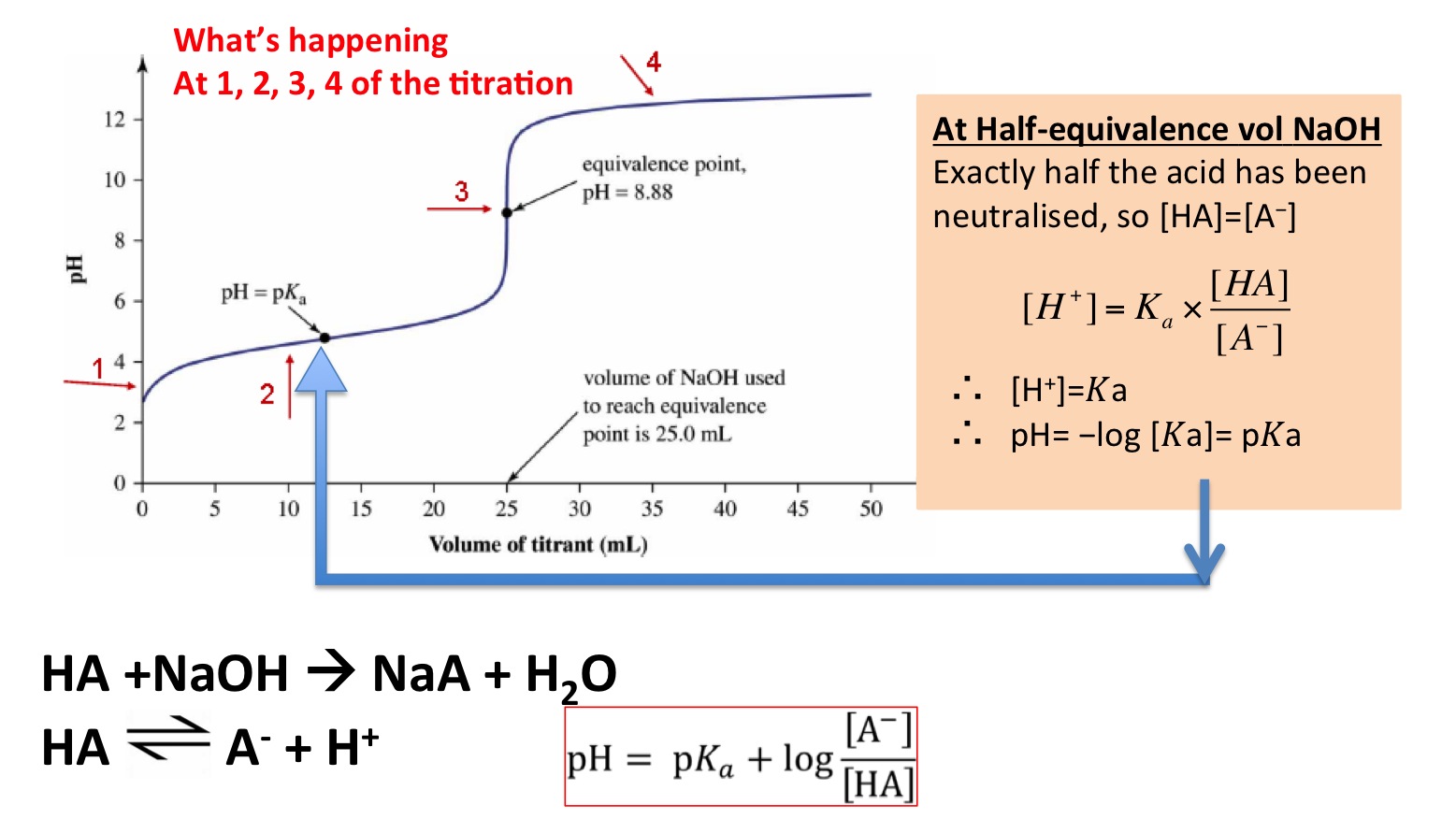
Since in our example the first equivalence point occurs at 25 mL the first half titration point occurs at 125 mL added which is highlighted in blue in the figure.
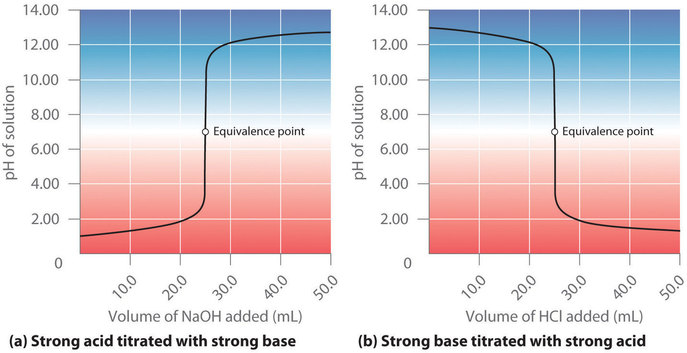
How to calculate the ph at equivalence point of titration. Running acid into the alkali You can see that the pH only falls a very small amount until quite near the equivalence point. For a strong acid and a weak base the pH will be. 2 The pH of the solution at equivalence point is dependent on the strength of the acid and strength of the base used in the titration.
For this reason you must select the correct indicator for the right combination of solutions as the range of colour changes needs to have the equivalence point. Then there is a really steep plunge. Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to understand the value of the pKa at the equivalence point.
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of a solution containing 1500 mg of ethylamine C_2H_5NH_2 with 01000 M. The pH of the resulting solution at equivalence point is given below. The excess can be calculated by subtracting initial moles of analyte B from moles of.
The K X b 44 10 4. If that number is greater than the number of moles of base B the titration is past the equivalence point. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is pH pKa log base acid.
Eqrm pH 7 dfrac12 left pK_a log salt right eq Answer and Explanation. This point on the curve corresponds to pK a1 4 which is indicated in red next to the pH axis. This is simple solution stoichiometry.
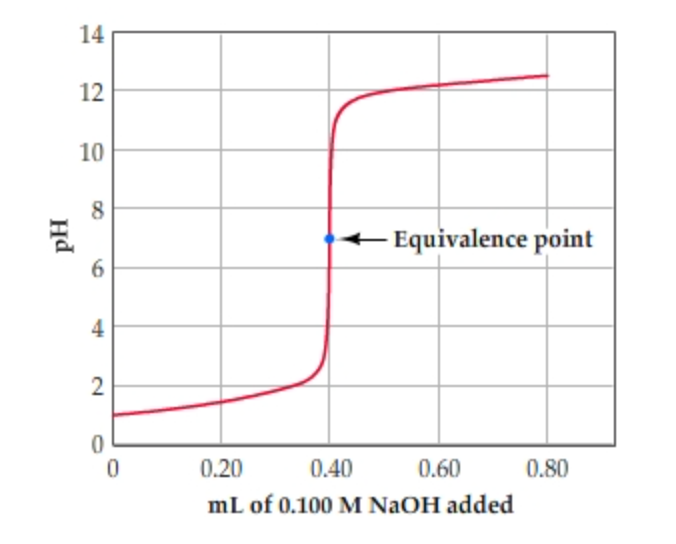
To find the pH first simply find the moles of excess H 3 O. The second half titration point occurs half way between the first equivalence point and the second equivalence point. -- For strong acid-strong base titration pH 7 at equivalence point.
The Ko of methylamine is 50 x 104. The pKa of the solution is the negative logarithm of the Ka. Suppose 100 mL of the 6 M strong acid titrant which comes out to 06 moles is added.
Therefore we can use the formula of weak base to calculate the OH-concentration at this equivalence point. The Kp of methylamine is 50 10-4. Concentration of CH 3 COO-can also be easily calculated keeping in mind the total volume is 50cm 3.
If you calculate the values the pH falls all the way from 113 when you have added 249 cm3to 27 when you have added 251 cm3. Solution for Calculate the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of 0100 M methylamine CHNH with 0100 M HC1. The equivalence point will occur at a pH within the pH range of the stronger solution ie.
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point of a titration of 62 mL of 01 M C H X 3 N H X 2 with 020 M HCl. That means we have to find pK b of conjugated base and calculate concentration of OH - starting from there then use pH14-pOH formula. K b is not given but we can calculate it easily from ionic product of water K w and K a via the formula K w K aK b.
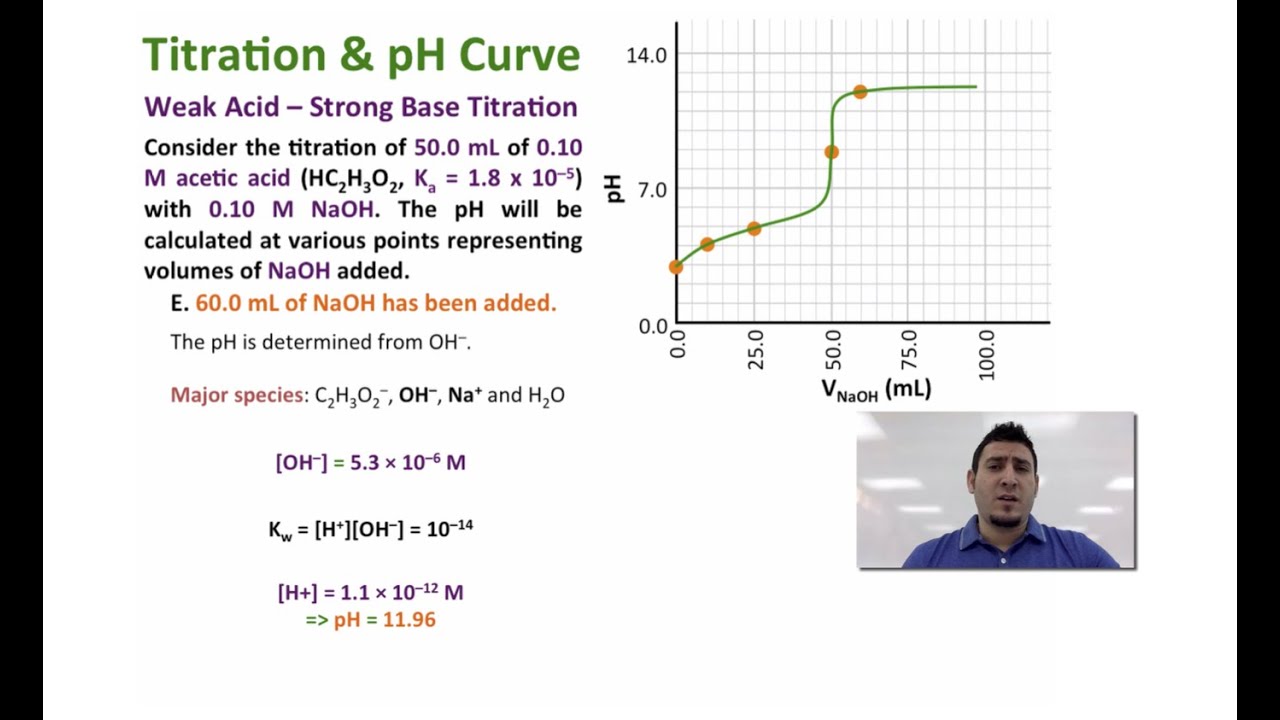
Strong acid strong base titration To reach equivalence point HNO 3 KOH H 2 Ol KNO 3 aq I 0100 moles each sampletitrant C End After equivalence point any excess strong base KOH determines the pH. After the equivalence point the stoichiometric reaction has neutralized all the sample and the pH depends on how much excess titrant has been added. We can now substitute these back into the weak base formula to find OH-concentration and eventually the pH at this equivalence point.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. PH 1458 Incorrect Calculate the pH for each of the cases in the titration of 250 mL of 0180 M pyridine CH Naq with 0180 M HBraq. -- For weak acid-strong base titration pH 7 at equivalence point.
At the equivalence point the moles of CH3NH2 equals the moles of HCl. Because these molecules do not fully dissociate the pH shifts less when near the equivalence point. At the equivalence point the concentrations of the base and the acid are equal.

17 4 Titrations And Ph Curves Chemistry Libretexts
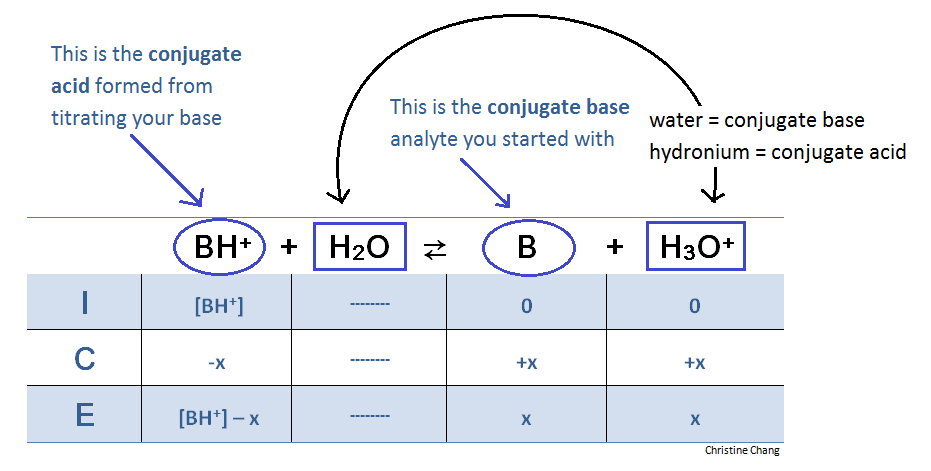
Titration Of A Weak Base With A Strong Acid Chemistry Libretexts

Calculate Ph At The Equivalence Point Youtube

Strong Acid Strong Base Titrations

Ib Chemistry Higher Level Notes Acid Base Calculations
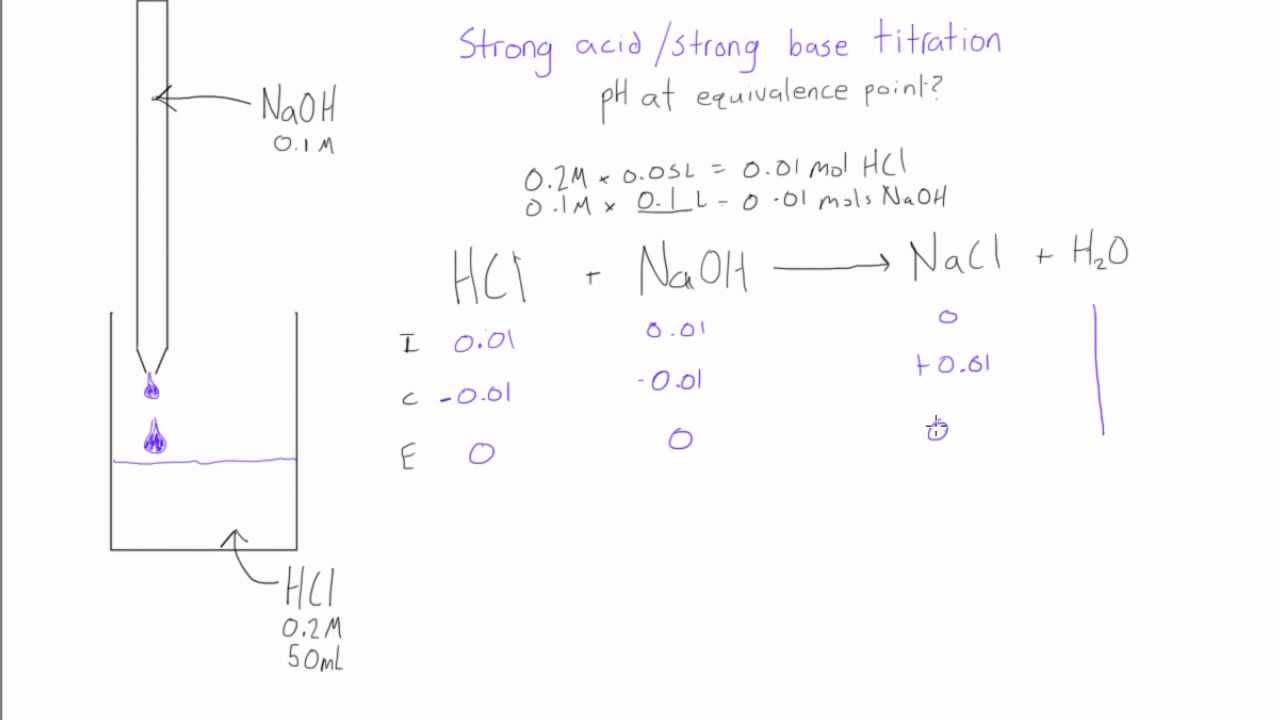
Strong Acid Strong Base Titration Ph At Equivalence Point Youtube

Strong Acid Strong Base Titration Ph After Equivalence Point Youtube

Calculate The Ph At One Half The Equivalence Point Youtube

Calculate The Ph At The Equivalence Point During The Titration Of 0 1m 25 Ml Ch 3 Cooh With 0 05m Naoh Solution K A Ch 3 Cooh 1 8 Xx 10 5

Acid Base Titrations Introduction 3 Overview Titrations Are Important Tools In Providing Quantitative And Qualitative Data For A Sample To Best Understand Ppt Download
In An Acid Base Titration How Do I Calculate The Ph At The Second Equivalence Point When Pka1 Is 4 5 And Pka2 Is 5 5 Against Naoh Quora
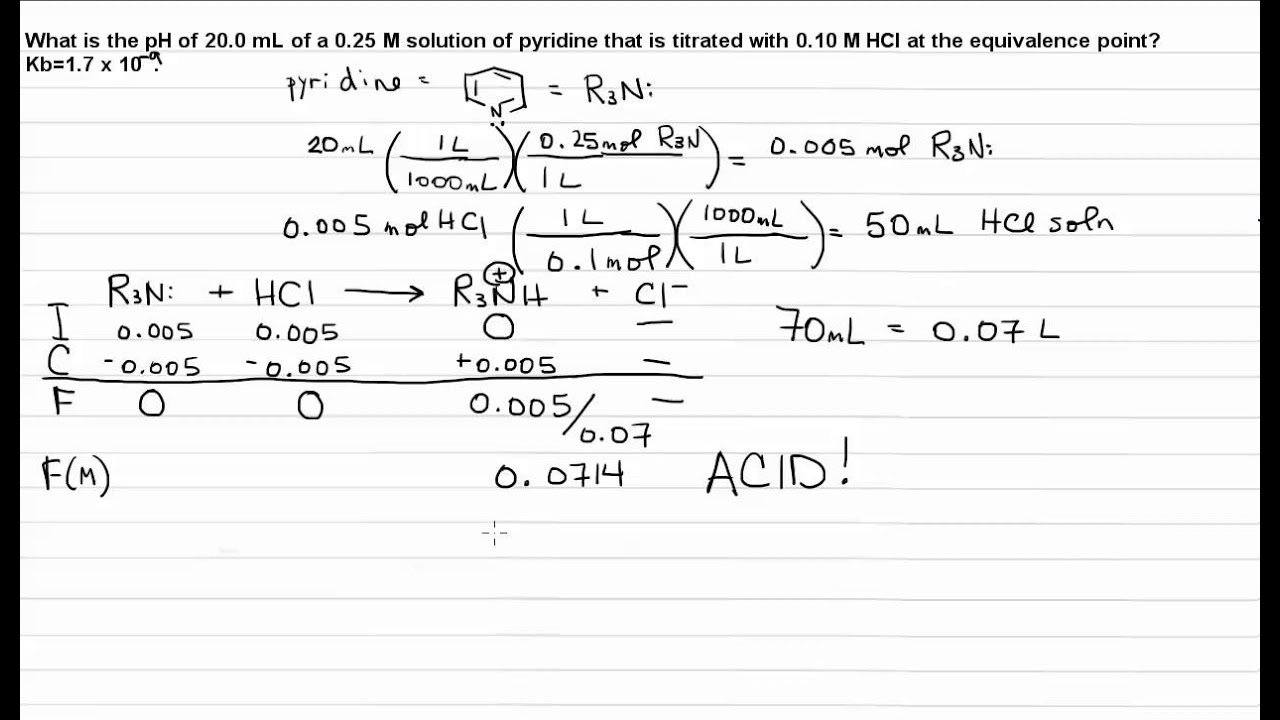
Titration Weak Base Strong Acid Equivalence Point Youtube
The Ph At One Half The Equivalence Point In An Acid Base Titration Was Found To Be 5 67 What Is The Value Of K A For This Unknown Acid Socratic

Strong Acid Strong Base Titration Ph Before Equivalence Point Youtube
How Do You Calculate The Ph At The Equivalence Point For The Titration Of 190m Methylamine With 190m Hcl The Kb Of Methylamine Is 5 0x10 4 Socratic

Ib Chemistry Higher Level Notes Acid Base Calculations

Chem 123 Titration Solving For Ph At Equivalence Point Youtube
Solved Learning Goal To Calculate The Ph At The Equivale Chegg Com
Post a Comment for "How To Calculate The Ph At Equivalence Point Of Titration"